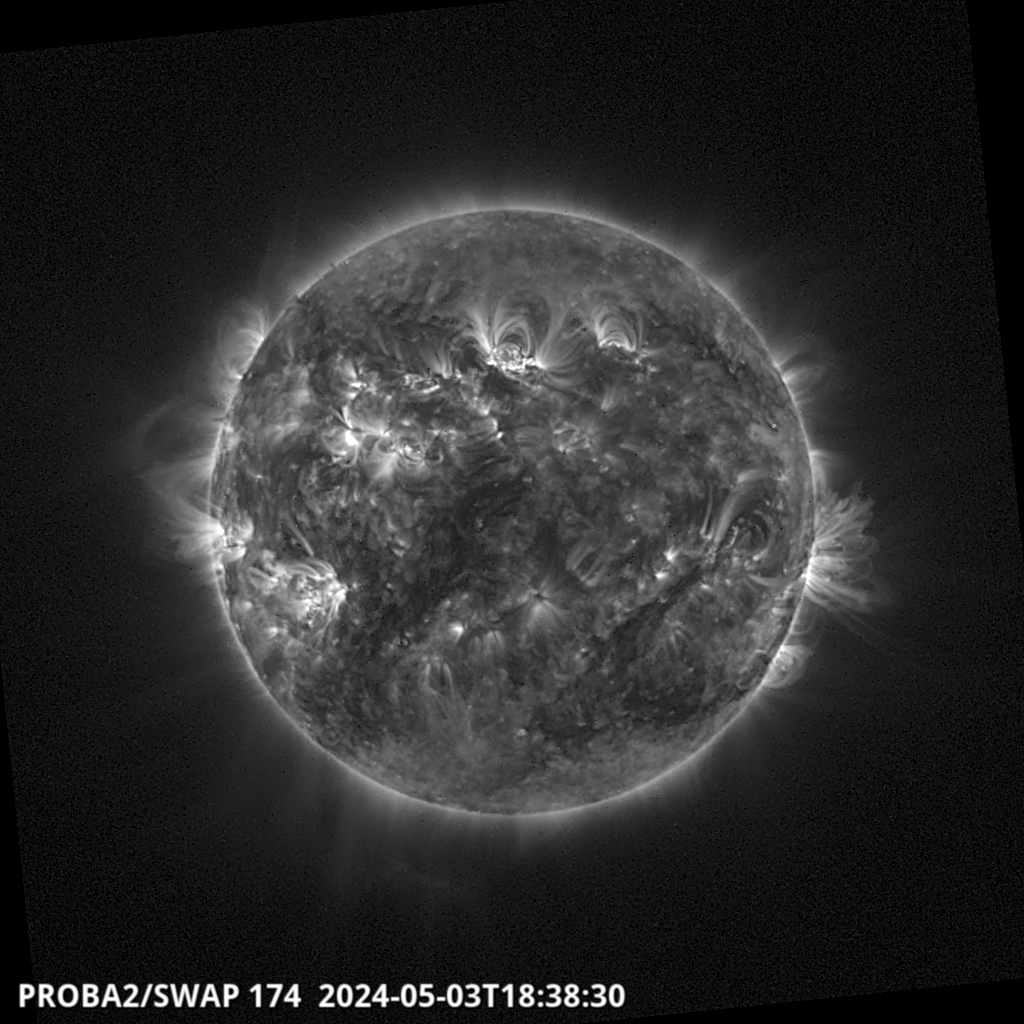
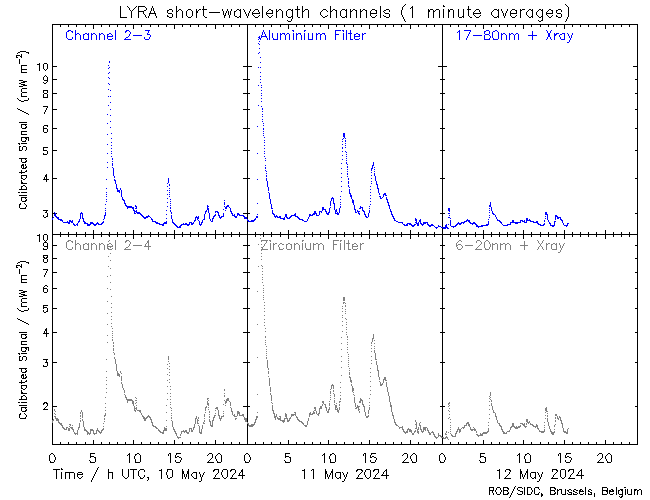
Solar flaring activity remained at high levels in the past 24 hours with multiple low M-class flares. There are 16 numbered and several unnumbered active regions on the visible solar disc. NOAA AR 3645 (beta-gamma) remains the largest region, while NOAA AR 3643 (beta-gamma-delta) and NOAA AR 3648 (beta-gamma-delta) became the most complex ones. NOAA AR 3639 (beta), NOAA AR 3646 (beta) and NOAA AR 3647 (beta) have decreased the complexity of their underlying magnetic field. The strongest activity was M2.0 flare, start time 22:54 UTC, end time 23:05 UTC, peak time 22:59 UTC on April 24th produced by NOAA AR 3637 (beta) from the west limb. The remaining M-class flaring was produced by NOAA AR 3645 and NOAA AR 3648. The solar flaring activity is expected to be at moderate to high levels over the next days with likely further M-class flaring and 25% chance for isolated X-class flaring.
No Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs) have been observed in coronagraph imagery over the past 24 hours. Type II and type IV radio bursts were reported related to C9.4-class flaring from NOAA AR 3638 14:10 UTC on April 24th. The resulting westward CME is estimated to have no impact on Earth.
A positive polarity mid-latitude coronal hole is currently residing on the central meridian in the southern hemisphere. The high speed stream emanating from it might arrive to Earth on April 28th, possibly superimposed with expected preceding high speed stream arrival.
Over the past 24 hours the greater than 10 MeV GOES proton flux was at background levels and is expected to continue so over the next days, pending any fast eruptive solar activity.
The greater than 2 MeV electron flux as measure by GOES 16 and GOES 18 has exceeded the1000 pfu threshold over the past 24h and is expected to repeatedly exceed the 1000 pfu threshold in the upcoming days. The 24h electron fluence was at boundary of nominal to moderate level and is expected to be at moderate levels for the upcoming days.