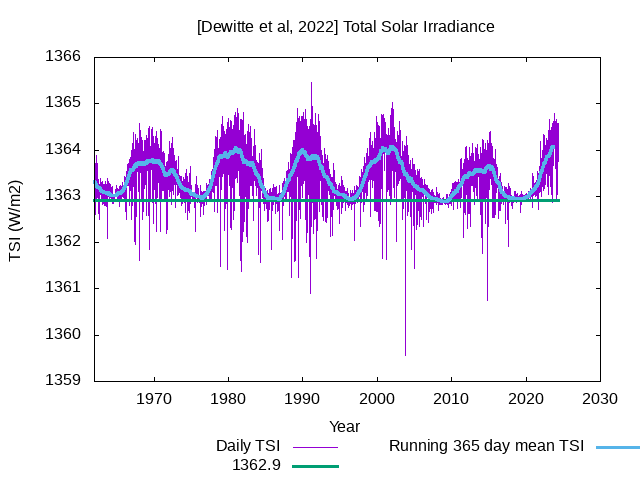
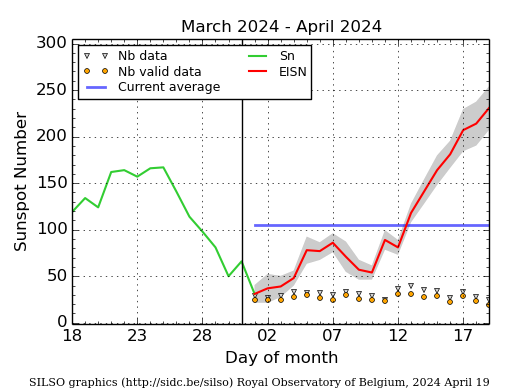
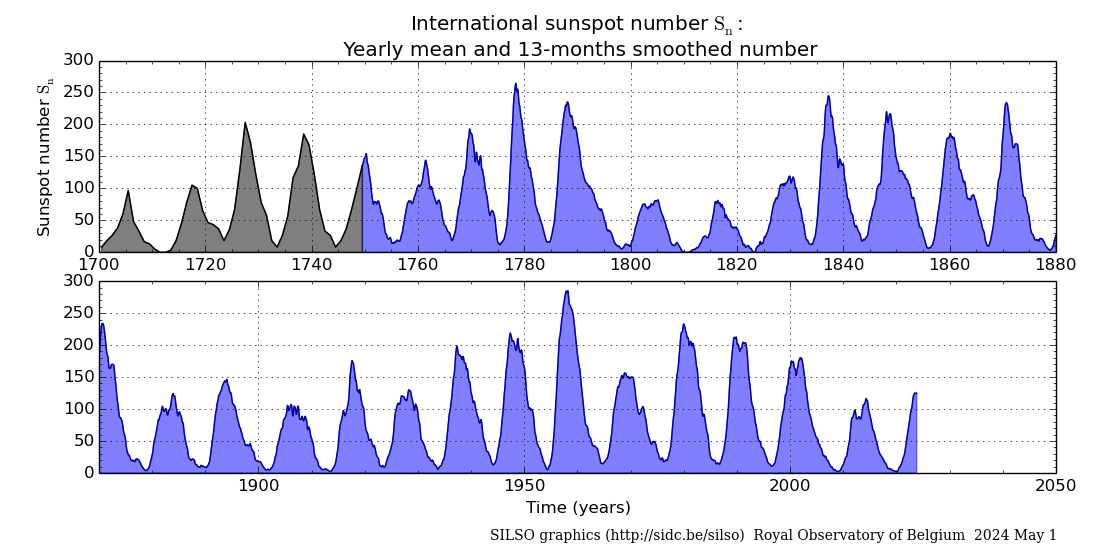
Research
Publications
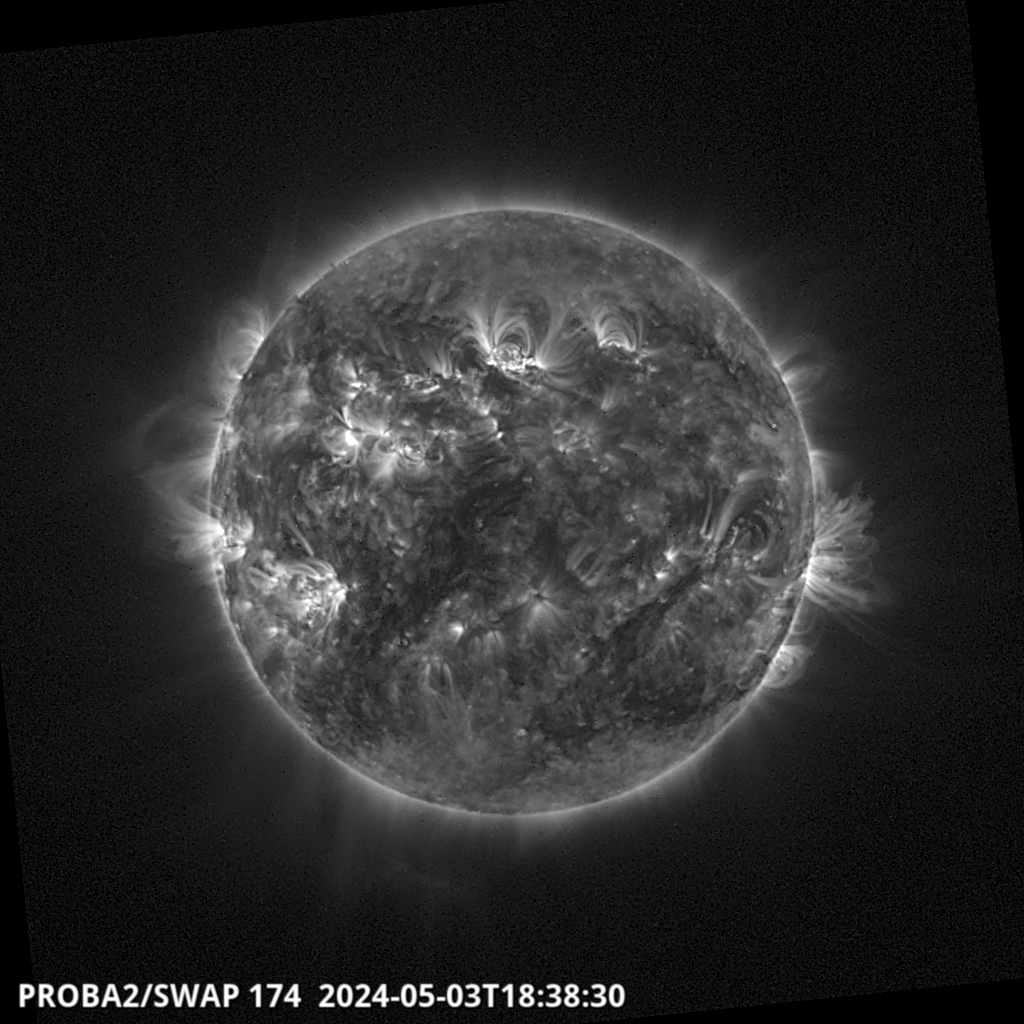
- The Sun's fluffy corona in exquisite detail
Henke, & al., 2024 - Statistical investigation of decayless oscillations in small-scale coronal loops observed by Solar Orbiter/EUI
Kumar Shrivastav, & al., 2024 - A rapid sequence of SEP events associated with a series of EUV jets: Solar Orbiter, STEREO-A and near-Earth spacecraft observations
Lario, & al., 2024 - Analysis of Coronal Mass Ejections through novel Extreme Ultraviolet Imager observations and modeling.
Dorsch, & al., 2024 - Investigating coronal loop morphology and dynamics from two vantage points
Mandal, & al., 2024
News

The King is dead, long live the King?
While NOAA 3664 has rounded the Sun's west limb, a new X-class flare producing active region has shown up near the Sun's east limb.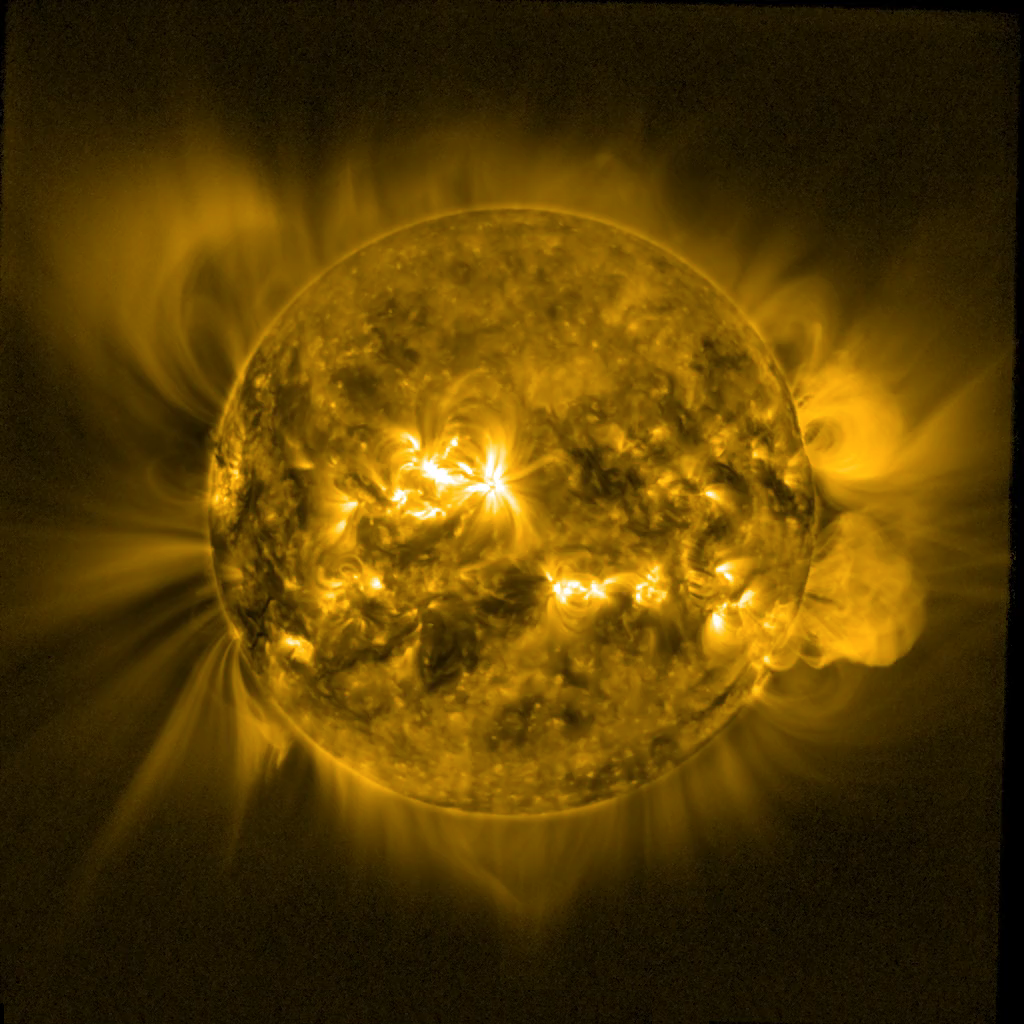
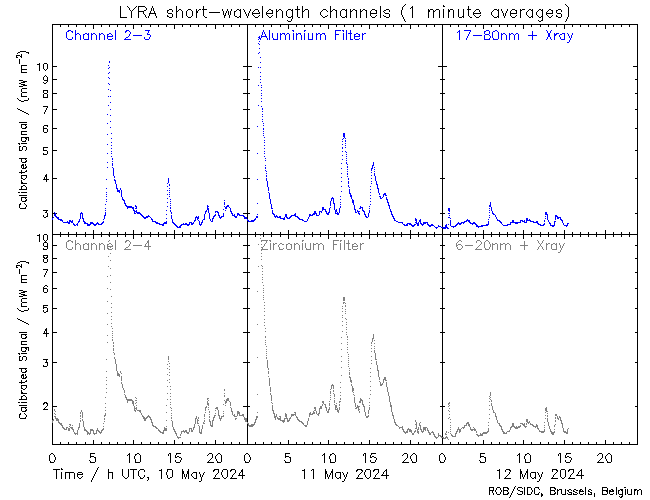
Sunspots and aurora
Last weekend's polar lights have been witnessed by millions around the world. While many drove to dark places to watch this celestial spectacle, others grabbed a lawn chair and watched the baffling show from their own backyard. Children were woken up by their parents to watch the colours in the sky. The 10-11 May aurora certainly captured the attention and awe of the public and the media.